Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding M3U Files: A Brief Overview
M3U files are a widely used format for creating M3u playlists, particularly in the realm of digital media streaming. Originating from the MPEG Audio Layer 3 (MP3) format, M3U stands for “Moving Picture Experts Group Audio Universal.” These text-based files contain paths to audio or video files, allowing media players to play multiple tracks in a specified order.
The structure is straightforward: each line typically points to a single media file, either through a local file path or an online URL, making M3U files versatile for both personal and shared playlists. They are commonly utilized in various applications, including Internet radio, video streaming services, and personal media libraries, catering to users who want to organize their media efficiently.
Understanding M3U files is essential for anyone looking to enhance their media experience, as they provide a simple way to curate and shares M3u playlists across different platforms. Additionally, many modern media players, such as VLC and Winamp, support M3U files, ensuring a seamless playback experience. By grasping the fundamentals of M3U files, users can unlock new possibilities for enjoying their favorite audio and video content in a structured and accessible manner.
The Structure of M3U Playlists
M3U playlist is a popular file format used for organizing and streaming multimedia content, primarily audio and video. The structure of an M3U playlists are straightforward yet effective, making it accessible for both beginners and experienced users.
An M3U file typically starts with a header line, which indicates the file type, followed by a series of entries, each representing a media file. Each entry can include metadata such as the duration, title, and even the artist, formatted in a specific way to enhance playback compatibility.
For instance, the first line might look like `#EXTM3U`, signaling the beginning of the playlist. Following that, you’ll often find lines beginning with `#EXTINF`, which provides details about the media duration and title before the URL of the media file itself. This efficient structure allows media players to quickly read and interpret the M3u playlist, ensuring smooth playback.
By understanding the M3U format video, users can create personalized playlists tailored to their preferences or even share them across devices, making it an invaluable tool for anyone looking to curate their listening or viewing experience. With the rise of streaming services, mastering the structure of playlists can significantly enhance how you manage and enjoy your media library.
Channel Grouping in M3U Lists
Channel grouping in M3U playlists is an essential practice for organizing and managing IPTV content effectively. An M3U file is essentially a playlist format that allows users to stream media from various sources, and proper channel grouping enhances the user experience by providing a seamless navigation structure.
By categorizing channels into specific groups such as “Sports,” “News,” “Movies,” and “Kids,” users can easily find their preferred content without sifting through long, cumbersome lists. This not only saves time but also reduces frustration, making the viewing experience more enjoyable.
For those creating or managing M3U playlist, using clear and descriptive group names is vital. Additionally, maintaining an updated list of active channels within each group ensures users have access to the latest and most relevant content. Advanced users can leverage software tools to automate the grouping process, ensuring that their M3U playlist remain organized as new channels are added.
Ultimately, effective channel grouping in playlist not only optimizes content accessibility but also enhances viewer satisfaction, making it a critical component of any IPTV service. By focusing on user needs and improving navigation, channel grouping transforms the way audiences interact with their favorite media.
Broadcasting Protocols Used in M3U
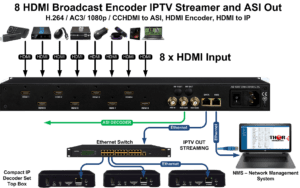
M3U files are pivotal in streaming media, serving as playlists for various multimedia content. One of the key broadcasting protocols used with M3U is HTTP Live Streaming (HLS), developed by Apple. HLS allows for adaptive bitrate streaming, enabling a seamless viewing experience by adjusting video quality based on the user’s bandwidth.
Another important protocol is Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP), which facilitates the delivery of live content over the internet with low latency, making it ideal for live broadcasts and interactive sessions. Moreover, the Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) protocol is gaining traction in M3U applications, as it offers enhanced flexibility in managing video streams across different devices. This versatility ensures compatibility with various platforms, from smart TVs to mobile devices. Additionally, protocols like MPEG-DASH and RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol) are often integrated, enhancing the overall streaming experience by optimizing data transfer and minimizing buffering.
Understanding these broadcasting protocols is crucial for content creators and broadcasters, as they directly impact the quality, reliability, and accessibility of streamed content. By leveraging these protocols effectively, users can ensure a superior viewing experience that meets the demands of today’s diverse digital landscape.
Compatibility of M3U Lists with Different Media Players
M3U playlist is widely recognized for their flexibility and compatibility with various media players like IPTV SMARTERS PRO, making them an invaluable asset for streaming enthusiasts. These playlists, which store the locations of multimedia files, can be effortlessly used across popular media players like VLC, Kodi, and Plex. VLC, for instance, not only supports M3U but also allows users to create and edit playlists, enhancing the overall streaming experience.
Kodi, on the other hand, excels in integrating M3U playlists, enabling users to access live TV and radio streams seamlessly. Plex, with its user-friendly interface, also accommodate playlists, allowing users to enjoy a diverse array of content from different sources without hassle.
However, it’s essential to note that while most modern media players support M3U, the functionality may vary. Certain players might not recognize specific codecs or formats included in the M3U file. Therefore, ensuring compatibility often requires checking the media player’s documentation or community forums for specific requirements or limitations. By understanding these nuances, users can optimize their streaming experience, ensuring smooth playback and access to a broad spectrum of entertainment options across their favorite media players.
Dynamic vs. Static M3U Playlists
Dynamic M3U playlist is designed to provide a flexible and adaptive streaming experience, automatically updating their content based on specific criteria such as user preferences or available media. This means that when new shows or movies are added to a streaming service, a dynamic playlist can reflect these changes in real-time, ensuring users always have access to the latest content. In contrast, static M3U playlists offer a fixed list of media that does not change unless manually edited.
While static playlists can be easier to set up and manage, they lack the versatility that many users seek in today’s fast-paced digital landscape. For instance, a dynamic playlists can curate content based on viewing habits, making it ideal for those who want personalized recommendations without the hassle of constant updates.
On the other hand, static playlist might be suitable for users who prefer a consistent lineup of their favorite shows or songs but may miss out on new offerings. Ultimately, the choice between dynamic and static M3U playlists hinges on the user’s needs for adaptability versus simplicity, making it crucial to understand the unique benefits and limitations of each type for an optimal viewing experience.
Best Practices for Organizing Channels in M3U
Organizing channels effectively in playlists is crucial for enhancing user experience and ensuring easy navigation. Start by categorizing channels based on genres, such as sports, news, entertainment, and movies. This method not only simplifies the search process but also helps users quickly locate their preferred content.
Use clear, descriptive names for each channel to avoid confusion; for example, instead of abbreviations, opt for full titles that indicate the type of content, like “CNN News” rather than just “CNN.”
Implementing a consistent numbering system can also aid in organization; for instance, prefixing each channel with a genre code followed by a sequential number (e.g., “SP01” for the first sports channel) allows for easier sorting and retrieval. Additionally, consider including local channels for specific regions, as this can attract a broader audience.
Regularly update your M3U file to remove inactive channels and add new content, ensuring that your playlist remains relevant and engaging. Lastly, maintaining a backup of your organized M3U playlists can safeguard against data loss and streamline updates in the future. By following these best practices, you can create a well-structured M3U channel list that enhances viewer satisfaction and engagement.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with M3U Broadcasting
When troubleshooting common issues with M3U broadcasting, it’s essential to identify the root causes of playback problems, buffering, and connection errors. First, check the M3U playlist file for broken links or incorrect URLs, as these are often the culprits behind streaming failures. Utilizing a playlist validator can help streamline this process, ensuring that all entries are functional.
Next, consider the compatibility of your media player with M3U files; not all players support the same codecs or formats, which can lead to playback issues. If you experience buffering, assess your internet connection speed—M3U streaming requires a stable and robust bandwidth to deliver content smoothly. Additionally, verify that your device’s firewall or antivirus software isn’t blocking the streaming service, as this can result in connection interruptions.
Regularly updating your media player and codecs can also resolve many common issues, enhancing playback performance. Lastly, consulting online forums and communities dedicated to M3U broadcasting can provide valuable insights and solutions from experienced users. By addressing these common issues methodically, you can significantly improve your M3U broadcasting experience, ensuring seamless access to your favorite content.
The Future of M3U Playlists in Streaming Technology
As streaming technology continues to evolve, M3U playlists are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of content delivery. These text-based files, which list multimedia resources, are integral to the functionality of various streaming services, allowing users to access a multitude of channels and on-demand content seamlessly.
With the rise of personalized viewing experiences, M3U playlists are increasingly being integrated into smart TVs and mobile applications, enabling users to curate their own media libraries tailored to their preferences. Moreover, advancements in cloud technology facilitate the storage and sharing of M3U playlists, making it easier for content creators and distributors to reach wider audiences.
As we look ahead, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into streaming platforms is set to enhance M3U playlist functionalities, allowing for smarter recommendations based on user behavior and viewing habits. This shift not only promises to improve user engagement but also presents significant opportunities for advertisers to target audiences more effectively. Ultimately, the future of M3U playlists in streaming technology is bright, as they become essential tools for content organization, personalization, and enhanced user experience in an increasingly competitive digital landscape.